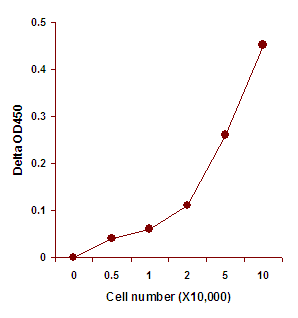
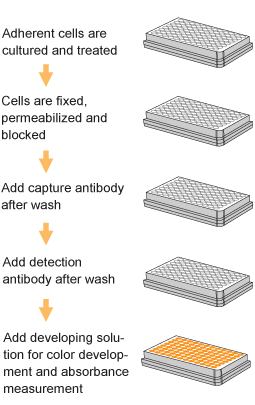
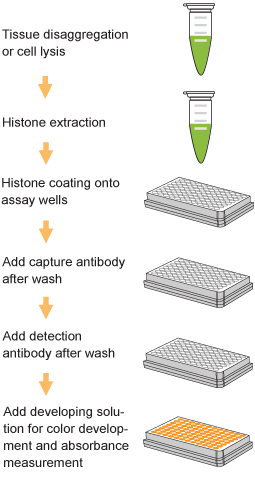
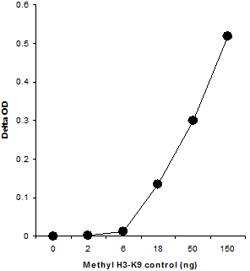
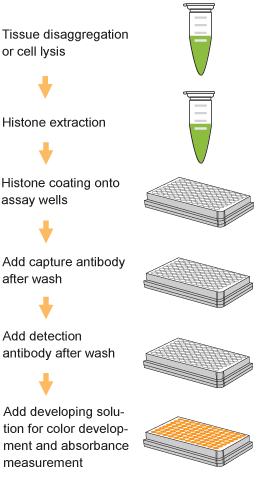
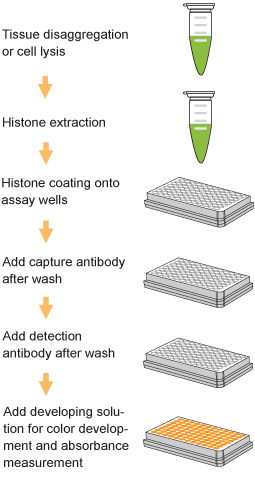
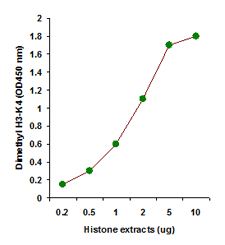
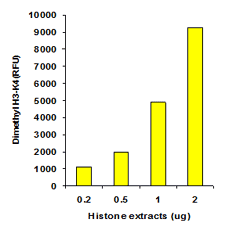
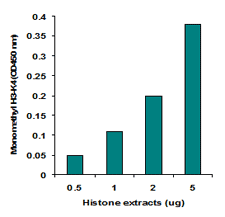
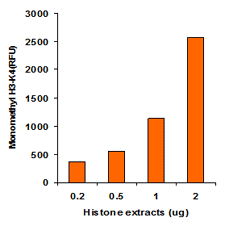
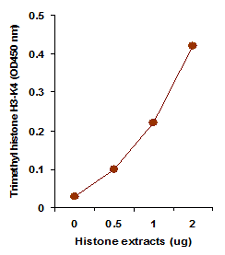
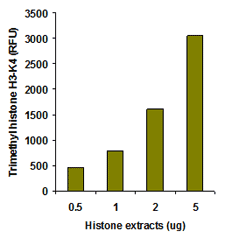
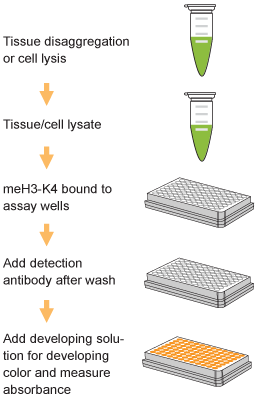
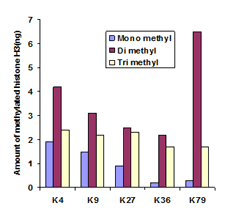
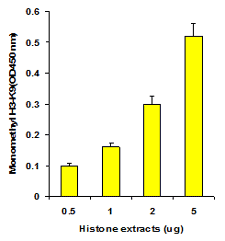
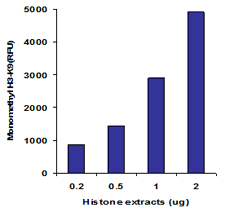
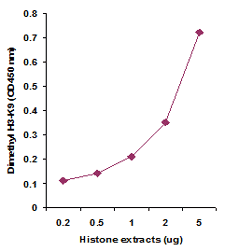
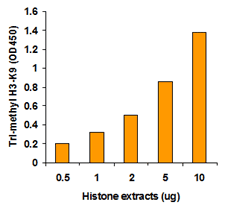
EpiQuik™ histone methylation assays are ELISA-based methods for quantifying global levels of the most important and well-characterized methylated H3/H4 marks from a variety of sample types, including cells (in situ), plasma, serum, and histone extracts.
The EpiQuik™ technology allows for rapid and efficient colorimetric detection of methylation modifications, conveniently eliminating the need for radioactivity, electrophoresis, or chromatography. Both singleplex and multiplex formats are available for either single modifications of interest or simultaneous screening of multiple modification patterns on the same plate.
EpigenTek delivers all-in-one resources to support and streamline your histone methylation quantification studies:
- Explore the Basics: Learn the fundamentals of Histone Methylation Quantification
- Additional Resources: Explore our detailed overview and supporting materials
- Technical Hub: Find FAQs, troubleshooting solutions, and optimization guides in our centralized support center




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)