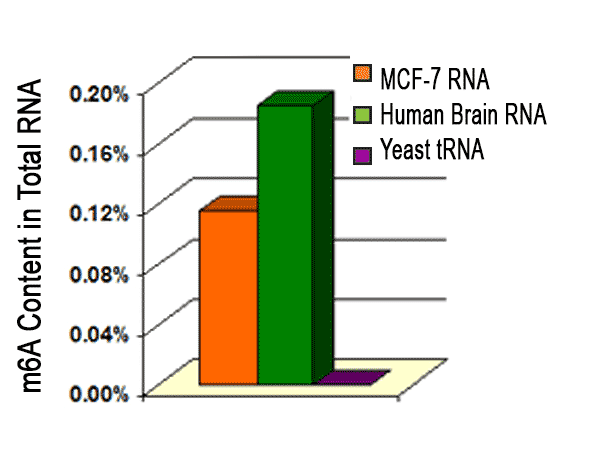
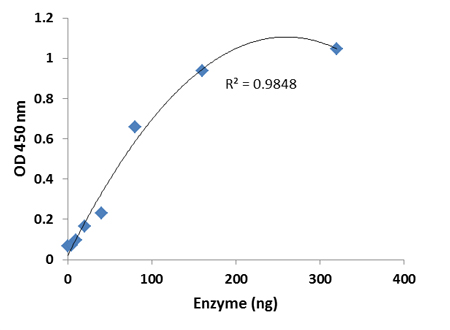
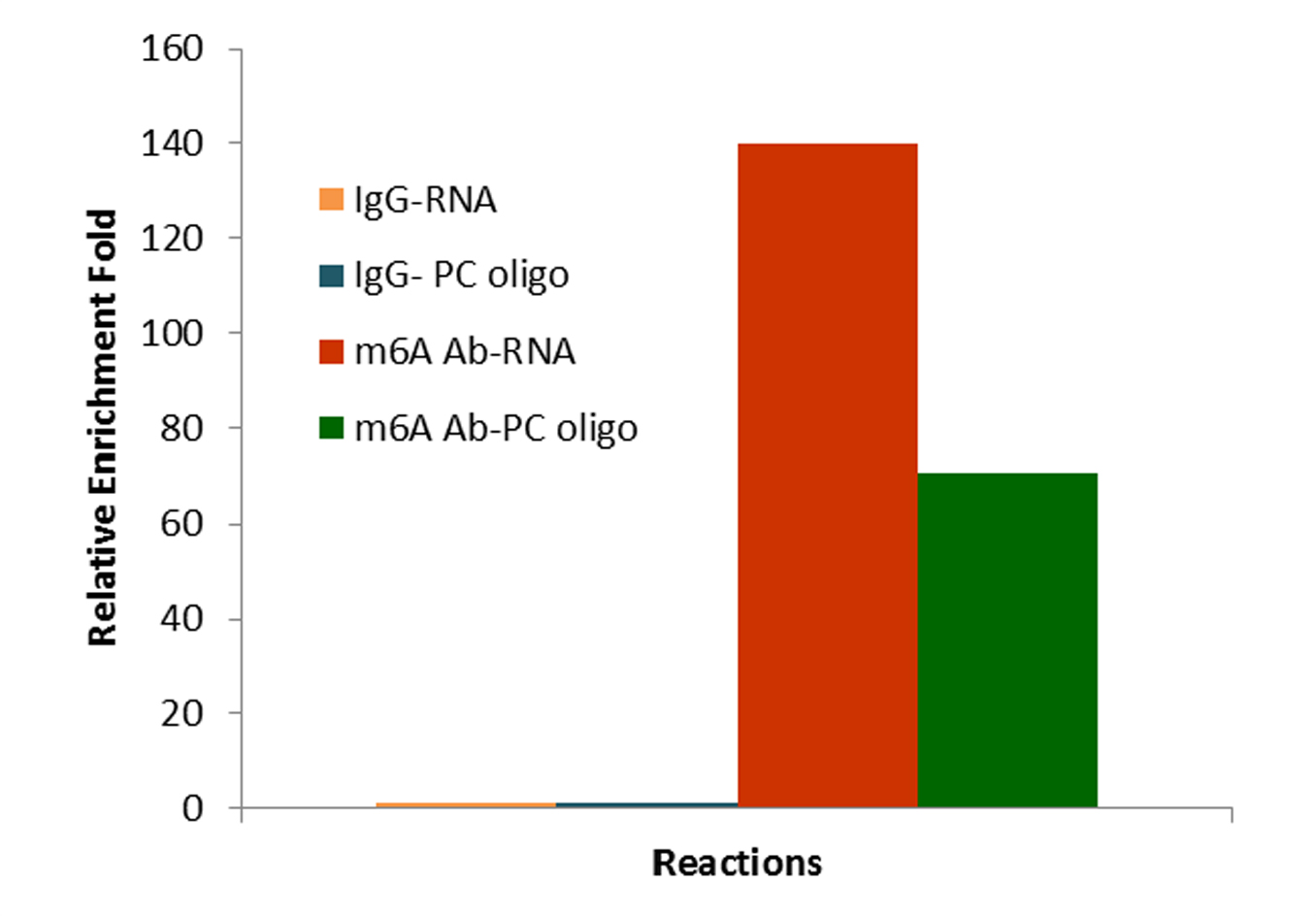
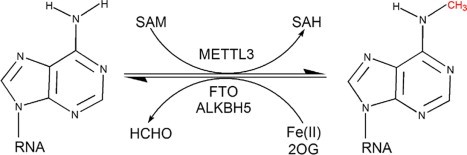
RNA methylation, such as N6-methyladenosine (m6A), is a key epigenetic modification where methyl groups are added to RNA nucleotides by RNA methyltransferases, like METTL3/14, influencing RNA stability, splicing, translation, and cellular function. This modification is reversible, as RNA demethylases, including FTO and ALKBH5, can remove methyl groups, allowing for dynamic regulation of gene expression.
Researchers study RNA methylation to understand its roles in development and diseases, as well as to explore its potential for novel therapeutic and diagnostic applications.
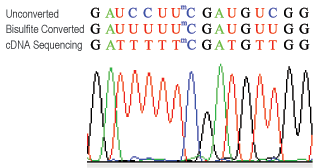
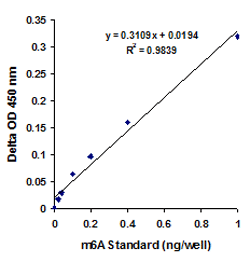
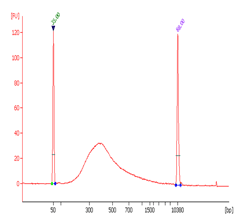
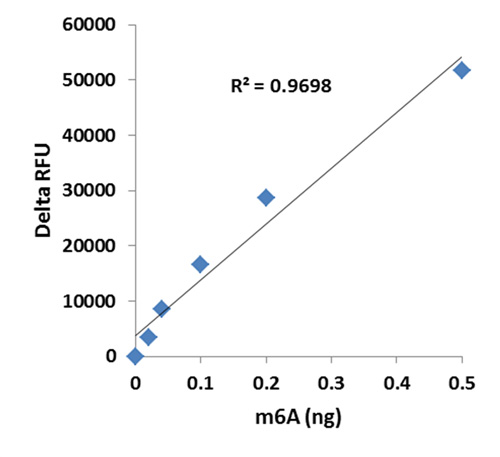
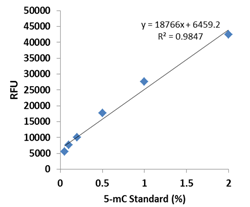
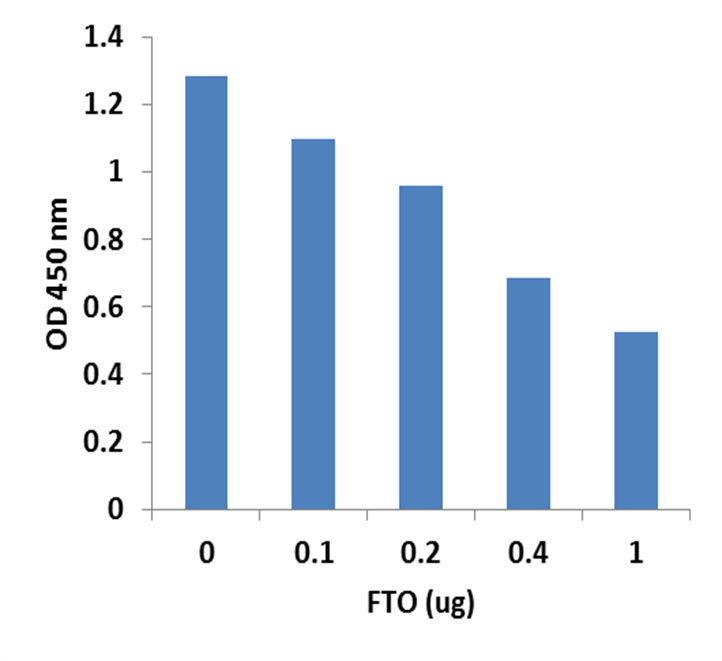
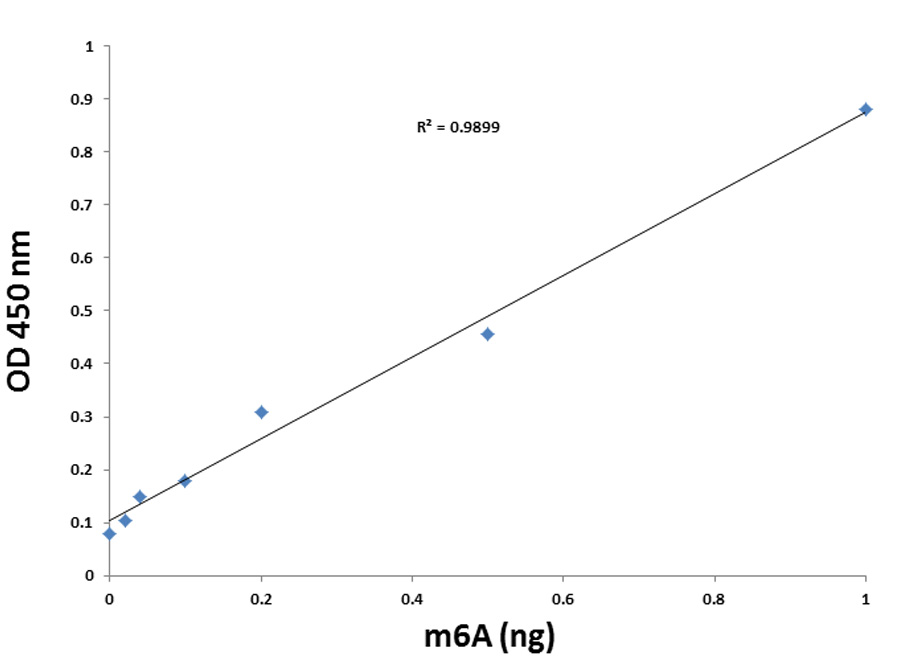
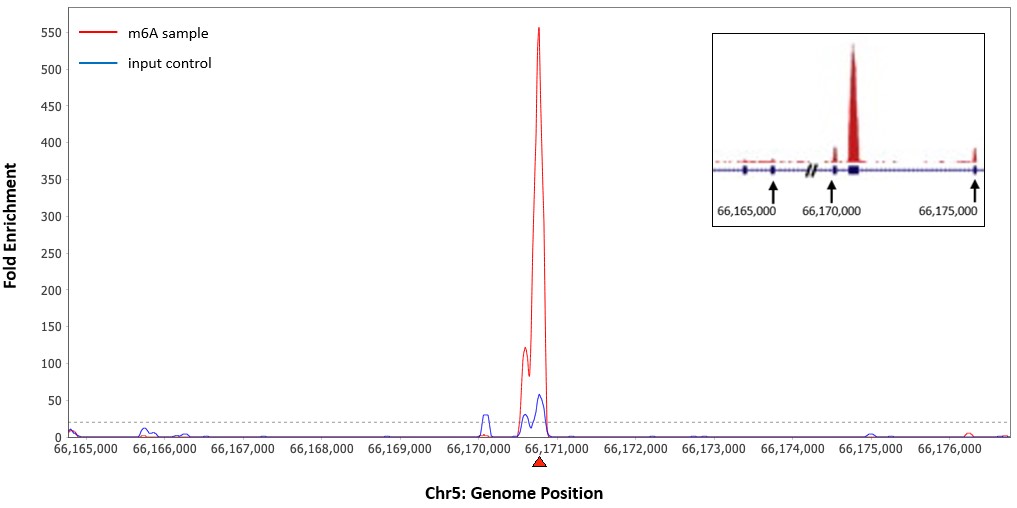
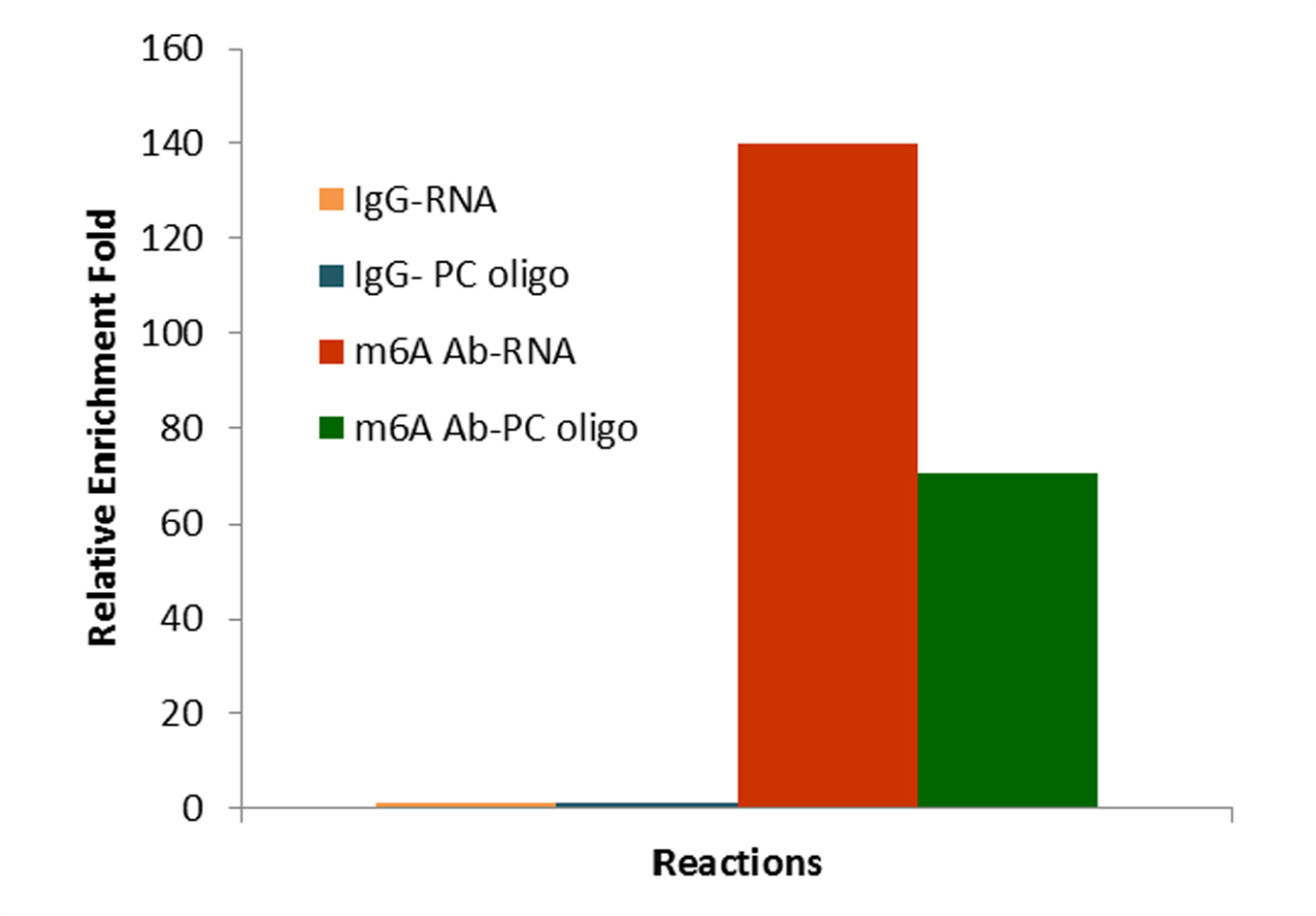
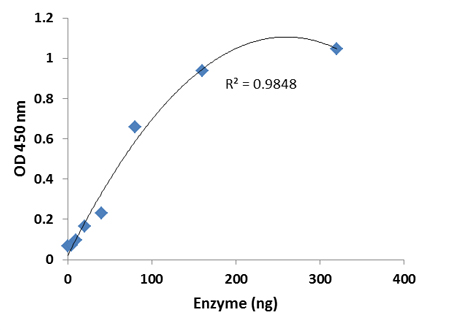
Bisulfite and CUT&RUN-based MeRIP assays for methylated RNA analysis




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)