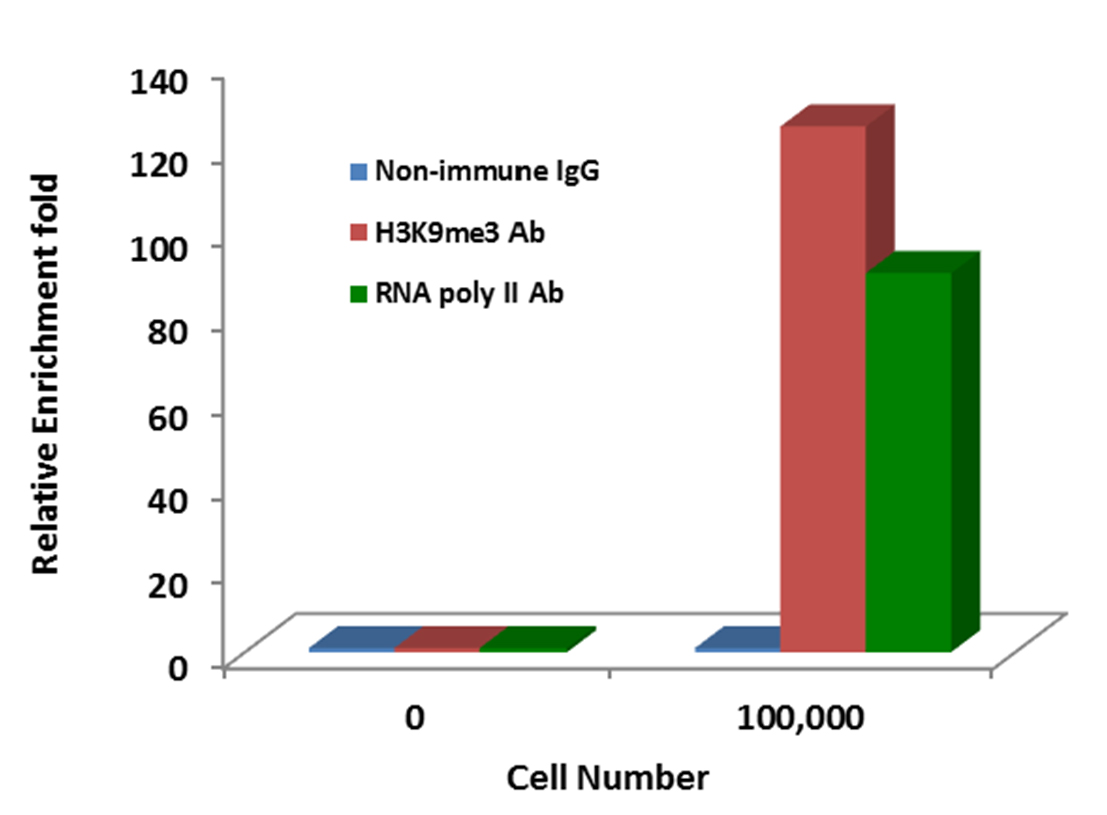
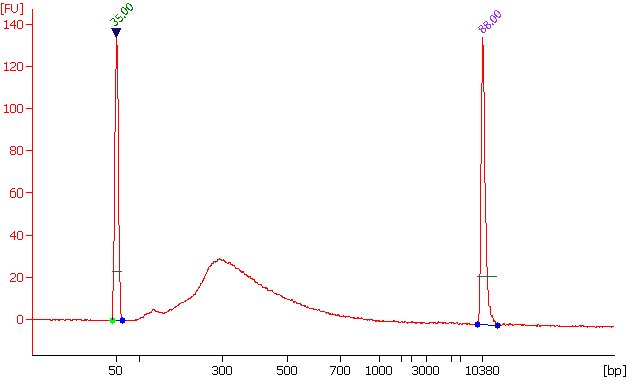
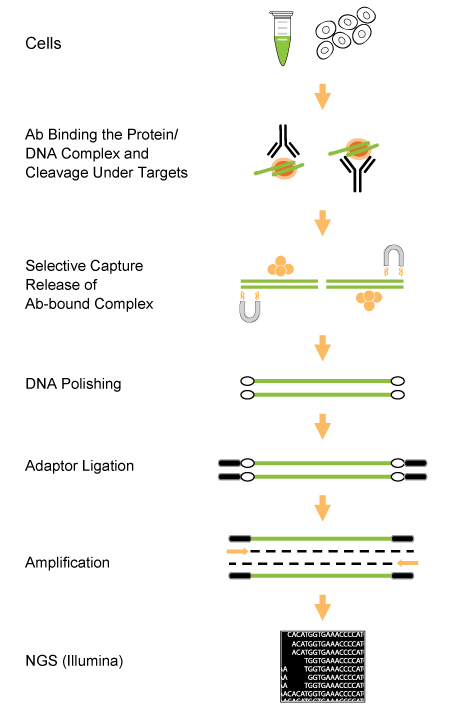
CUT&LUNCH (Cleavage Under Target and Liberate Unique Nucleic Complex Homogeneously) is an advanced chromatin profiling technique that enables high-resolution and highly sensitive mapping of histone post-translational modifications (PTMs) and chromatin-bound proteins, such as transcription factors.
The CUT&LUNCH assay significantly lowers input needs, processing time, and background signal compared to conventional ChIP and CUT&RUN, providing more reliable epigenomic profiles.
EpigenTek delivers all-in-one CUT&LUNCH and other resources to support and streamline your DNA–protein interaction studies:
- Explore the Basics: Learn the fundamentals of CUT&LUNCH
- Additional Resources: Explore our detailed overview and supporting materials
- Technical Hub: Find FAQs, troubleshooting solutions, and optimization guides in our centralized support center




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)