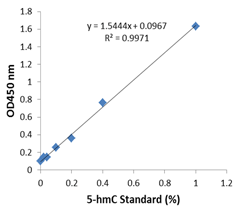
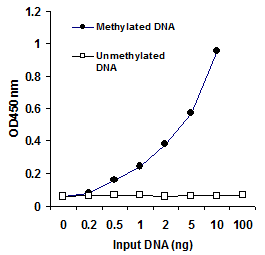
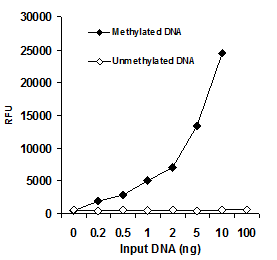
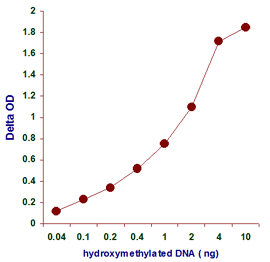
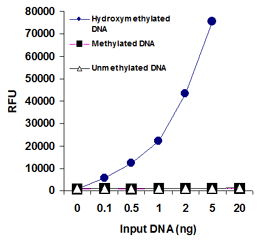
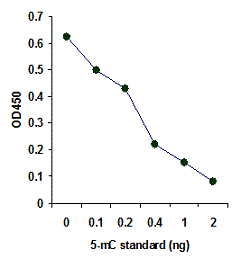
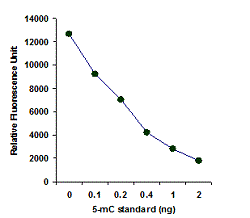
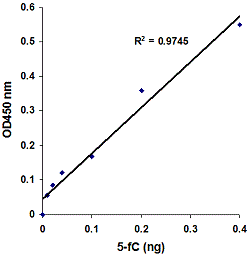
MethylFlash™ DNA methylation assays are ELISA-based methods for quantifying global levels of 5-mC, 5-hmC, and other modifications from intact DNA.
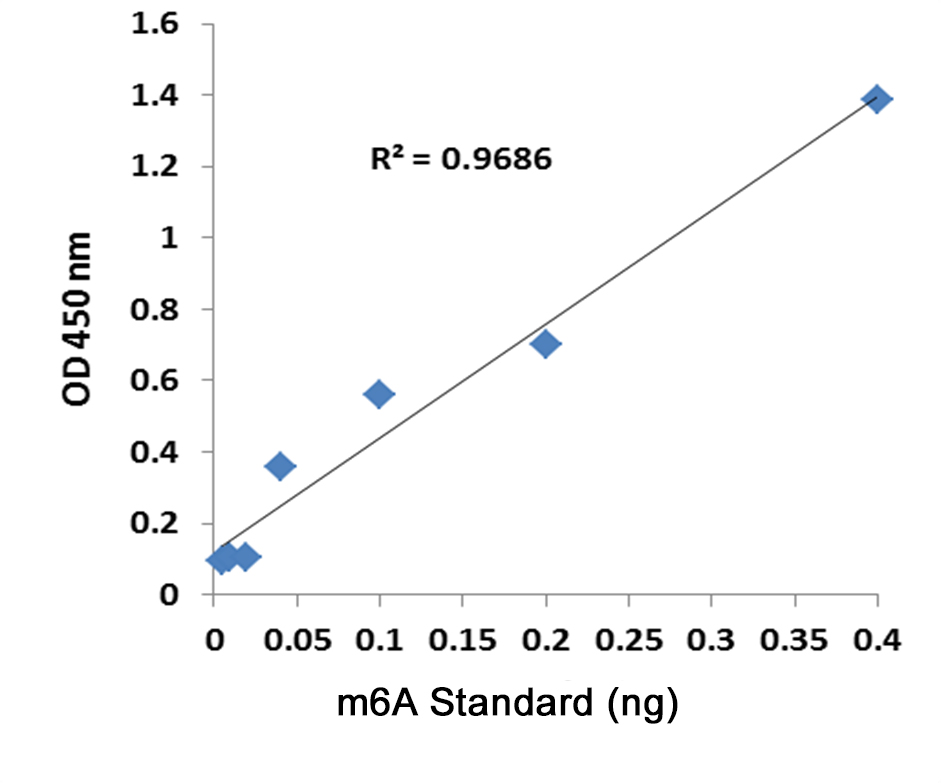
The MethylFlash™ technology allows for binding of sample DNA from any species directly to the assay plate wells, conveniently eliminating the need for DNA denaturation and plate blocking steps. Assay accuracy and sensitivity are benchmarked against gold-standard HPLC-MS analysis.
EpigenTek delivers all-in-one resources to support and streamline your global DNA methylation quantification studies:
- Explore the Basics: Learn the fundamentals of Global DNA Methylation Quantification
- Additional Resources: Explore our detailed overview and supporting materials
- Technical Hub: Find FAQs, troubleshooting solutions, and optimization guides in our centralized support center




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)