Epigenetics has long been recognized as a key player in regulating gene activity, with modifications to DNA and histones controlling the accessibility of genetic information. In recent years, the study of RNA modifications—often referred to as the "epitranscriptome"—has expanded our understanding of how post-transcriptional regulation shapes gene expression. Among the numerous chemical alterations identified on RNA, N6-methyladenosine (m6A) has emerged as the most abundant and dynamic mark on eukaryotic mRNA. Its roles in cellular processes and disease development have made m6A a critical focus of modern molecular biology.
The Importance of m6A RNA Methylation
The m6A modification involves the methylation of the nitrogen-6 position of adenosine residues in RNA. This process is catalyzed by a "writer" complex, primarily consisting of METTL proteins. Once deposited, m6A marks are recognized by "reader" proteins, such as YTH domain-containing proteins, which mediate downstream functions. Conversely, demethylases like FTO and ALKBH5 serve as "erasers," dynamically removing m6A marks to fine-tune RNA metabolism
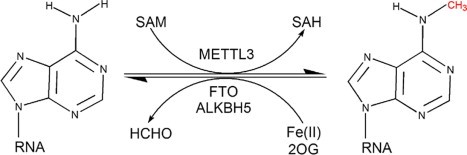
Functionally, m6A affects nearly every aspect of RNA biology, including splicing, stability, nuclear export, and translation. This regulatory flexibility enables cells to adapt to developmental cues and environmental stresses. Dysregulation of m6A pathways has been implicated in diseases like cancer, neurodegeneration, and metabolic disorders, underscoring the importance of accurately identifying and mapping m6A sites on RNA.

MeRIP with CUT&RUN
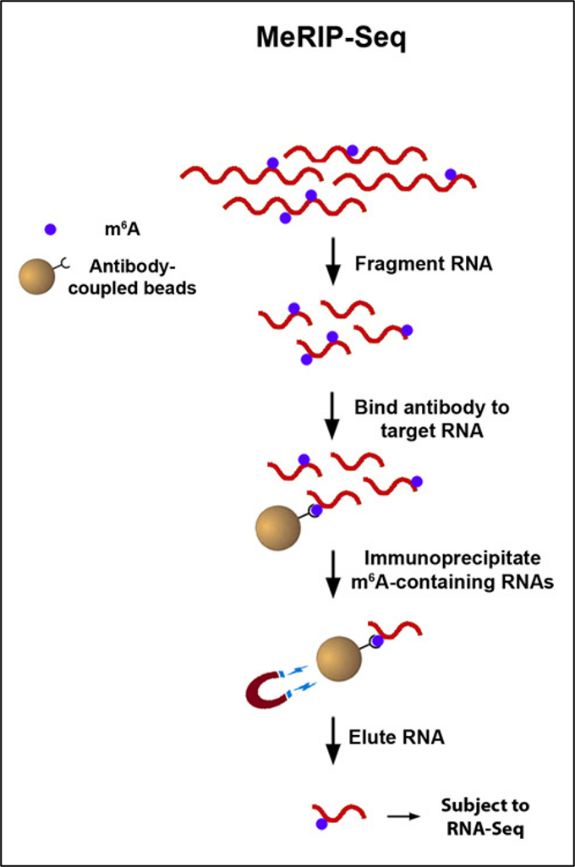
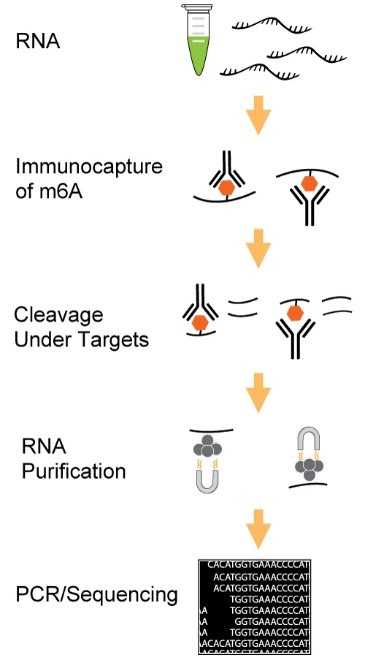
Traditional approaches for mapping m6A rely on methylated RNA immunoprecipitation (MeRIP), wherein an anti-m6A antibody enriches methylated RNA fragments. However, these methods often suffer from limitations such as background noise, poor resolution, and sample loss, especially when working with low RNA input. To address these challenges, EpigenTek has innovatively integrated the advantages of cleavage under targets and release using nuclease (CUT&RUN) into their MeRIP workflows, enabling researchers to achieve unparalleled precision and efficiency in m6A RNA enrichment.
EpigenTek's Solutions for m6A Research
The EpiQuik™ CUT&RUN m6A RNA Enrichment (MeRIP) Kit streamlines the enrichment of m6A-modified RNA via a CUT&RUN-based approach, ensuring high-resolution identification of m6A sites. For scientists aiming to perform both m6A RNA enrichment and NGS library preparation, the EpiNext™ CUT&RUN RNA m6A-Seq Kit offers an all-in-one solution. It incorporates all the benefits of the EpiQuik™ MeRIP Kit and adds NGS library preparation capabilities. Key features include:
- CUT&RUN-Based Enrichment: Unique integration of the advantages of CUT&RUN enhances fold enrichment, providing superior data quality compared to conventional MeRIP methods.
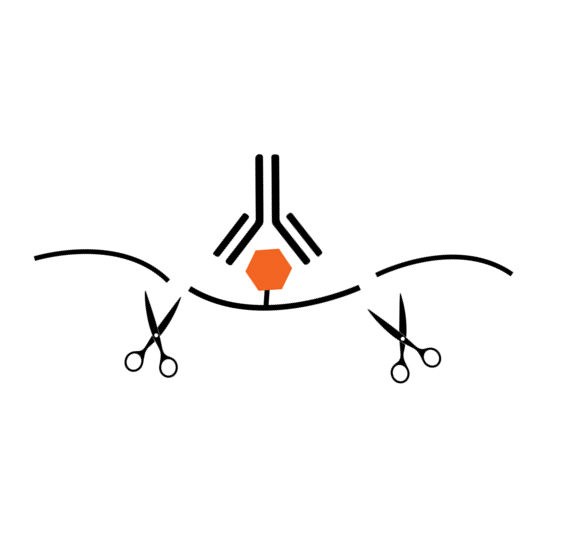
- Minimal Background: Uses a unique RNA cleavage enzyme mix to simultaneously fragment RNA and cleave/remove any RNA sequences at both ends of the target m6A -containing sequences without affecting RNA regions occupied by the antibody. Short RNA fragments are generated only bound with anti-m6A antibody. True target m6A-enriched regions can therefore be reliably identified and high-resolution mapping achieved.
- Low Input Requirement: Processes RNA input as low as 500 ng, minimizing sample loss while maintaining robust enrichment.
- Rapid Protocol: Achieves RNA to enriched m6A RNA in approximately 2.5 hours with less than 30 minutes of hands-on time, or RNA to library cDNA preparation in under 6 hours with less than 1 hour of hands-on time.
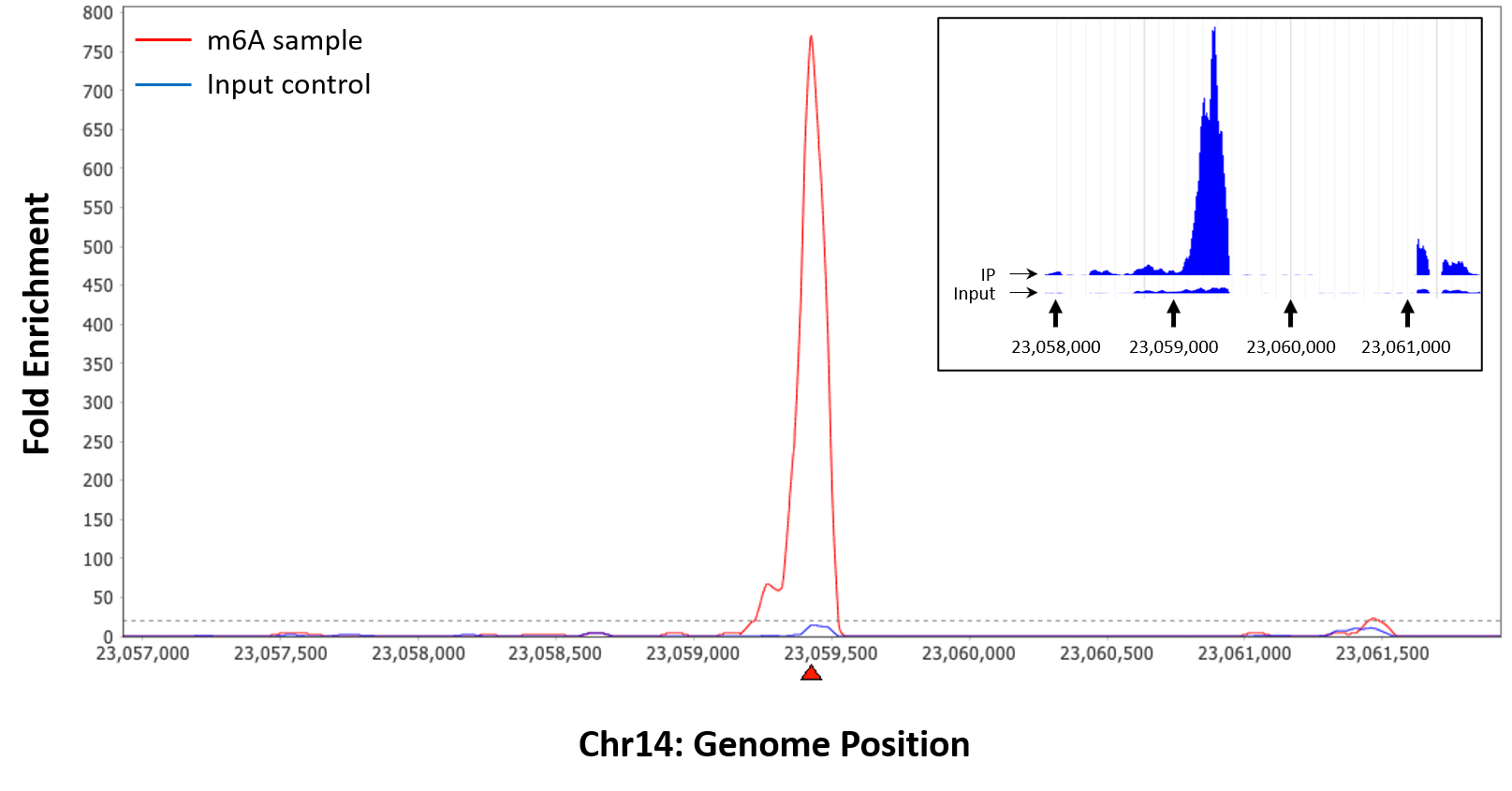
EpigenTek’s MeRIP and MeRIP-seq kits are the only products on the market to incorporate a CUT&RUN-based approach for m6A RNA enrichment. Our dedication to innovation ensures that researchers can push the boundaries of epitranscriptomics with confidence. Visit the EpiQuik™ CUT&RUN m6A Enrichment (MeRIP) Kit and EpiNext™ CUT&RUN RNA m6A-Seq Kit pages for more information and to accelerate your RNA methylation research today.
Refrences
- Niu Y, Zhao X, Wu YS, Li MM, Wang XJ, Yang YG. N6-methyl-adenosine (m6A) in RNA: an old modification with a novel epigenetic function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2013;11(1):8-17. doi:10.1016/j.gpb.2012.12.002
- Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3' UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149(7):1635-1646. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.003




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)