When most people think of gut bacteria, they imagine digestion or immune defense. But in recent years, scientists have uncovered that these tiny organisms do far more than break down food—they produce essential nutrients that influence how our bodies function at the deepest molecular levels. One of these nutrients, an amino acid called methionine, is at the center of new research exploring how gut microbes help regulate reproduction.
Why RNA Methylation Matters
Among the many ways cells regulate gene activity, RNA methylation—especially the m6A modification—has emerged as one of the most important. By adding small chemical tags to RNA molecules, cells can control how genes are read and translated into proteins. This process influences everything from cell growth and metabolism to brain development and fertility. When RNA methylation is disrupted, it can lead to problems in development, disease, and even reproductive health.
What the Researchers Set Out to Discover
In a study published in Cell Reports, scientists investigated whether a type of friendly gut bacterium could shape reproductive health through epigenetic pathways. They focused on methionine—a nutrient produced by microbes—as a possible driver of RNA methylation, the process that fine-tunes gene activity, including genes tied to metabolism and reproduction.
Inside the Study
To test their hypothesis, the researchers focused on a commensal gut bacterium called Enterobacter hormaechei. This bacterium produces methionine, which cells can then use to carry out RNA methylation. The team conducted experiments in the fruit fly Bactrocera dorsalis as their model organism, giving them a controlled way to examine how microbial methionine impacts reproduction. They were particularly interested in how this process affects the insulin receptor, a critical protein that helps regulate metabolism and reproductive function.
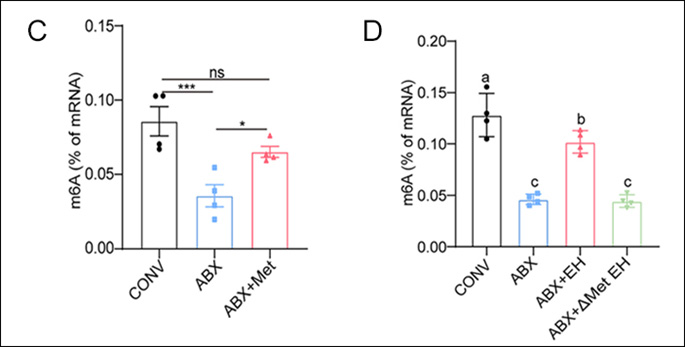
To measure global levels of RNA methylation, the team turned to EpigenTek’s EpiQuik™ m6A RNA Methylation Quantification Kit. The kit gave them a fast, reliable way to quantify m6A levels directly from their RNA samples without requiring complicated or time-consuming steps. Using the kit, the researchers confirmed that methionine from gut bacteria boosted m6A methylation on the insulin receptor’s RNA.
The Findings
The findings were striking: methionine produced by gut bacteria wasn’t just a nutrient—it was essential for proper m6A RNA methylation. Without it, the insulin receptor could not be regulated efficiently, which in turn impaired reproductive health. In simple terms, gut bacteria were shown to support reproduction by fine-tuning RNA at the molecular level. This study not only underscores the importance of the gut microbiome but also reveals a new epigenetic link between diet, microbes, and fertility.
Bringing It Back to the Lab
For researchers studying RNA methylation, tools that are both precise and convenient are essential. That’s why the scientists in this study used the EpiQuik™ m6A RNA Methylation Quantification Kit—a trusted solution for accurately measuring global m6A levels across different RNA types. Whether you’re studying metabolic pathways, reproductive health, or broader epigenetic mechanisms, our RNA methylation kits are designed to help you generate reproducible results with ease.
Explore our full line of RNA methylation kits and discover how EpigenTek can support your next breakthrough in epigenetics research.




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)