Pancreatic cancer remains one of the deadliest cancers worldwide, with late diagnosis, aggressive biology, and limited treatment options leading to poor patient outcomes. Resistance to frontline chemotherapy drugs such as gemcitabine further complicates management and underscores the urgent need to uncover new molecular mechanisms driving tumor survival.
m6A RNA Methylation in Cancer
In recent years, researchers have increasingly turned their focus to N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation, the most prevalent internal RNA modification in mammalian cells. m6A regulates RNA stability, splicing, transport, and translation, and alterations in m6A machinery are now known to play key roles in cancer development, progression, and drug resistance. Understanding how m6A modifications contribute to pancreatic cancer is vital for uncovering new therapeutic strategies.
EpigenTek Kits Powering RNA Methylation Research
To explore the role of m6A in pancreatic cancer, researchers combined both global m6A quantification and transcript-specific mapping approaches. For these analyses, they utilized two highly specialized EpigenTek kits:
- EpiQuik™ m6A RNA Methylation Quantification Kit (Colorimetric): Used to measure global m6A levels across pancreatic cancer cell samples.
- EpiQuik™ CUT&RUN m6A RNA Enrichment (MeRIP) Kit: Applied to perform MeRIP-qPCR, allowing precise enrichment and detection of m6A-modified transcripts.
Both tools offered the sensitivity, reproducibility, and specificity required to examine RNA methylation in challenging cancer models.
How the Study Was Conducted
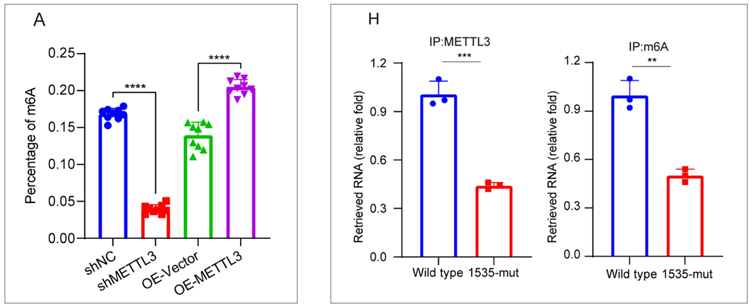
Using EpigenTek’s m6A RNA methylation quantification kit, researchers first detected the effect of METTL3 on global m6A levels in pancreatic cancer cells. They then applied the CUT&RUN m6A MeRIP kit to focus on specific targets, uncovering that the RNA methyltransferase METTL3 plays a critical role in regulating m6A deposition on transcripts such as HMGB1. Elevated m6A levels on these transcripts led to their degradation, which ultimately suppressed ferroptosis (a type of programmed cell death) and increased resistance to gemcitabine.
A key discovery was that O-GlcNAcylation, a sugar-based protein modification, stabilizes METTL3 by preventing its degradation. This modification, along with ubiquitination, ensured that METTL3 remained active in pancreatic cancer cells. The result was persistent m6A methylation activity, fueling tumor survival and drug resistance.
Overall Findings
The study demonstrated that O-GlcNAcylation and ubiquitination stabilize METTL3, driving enhanced m6A RNA methylation in pancreatic cancer. This stability allows cancer cells to silence transcripts like HMGB1 that would otherwise trigger ferroptosis, thereby promoting both tumor growth and resistance to chemotherapy.
Why Studying m6A Matters
These findings highlight the critical role of RNA modifications in cancer biology. m6A not only shapes how cells interpret genetic information but also acts as a molecular switch that can determine whether a cancer cell lives or dies under therapeutic stress. As epitranscriptomics continues to emerge, studying m6A offers a powerful window into disease mechanisms and provides potential new avenues for therapy.
EpigenTek: Trusted Tools for RNA Methylation
This work demonstrates how advanced RNA methylation tools, like the EpiQuik™ m6A RNA Methylation Quantification Kit and EpiQuik™ CUT&RUN m6A RNA Enrichment (MeRIP) Kit, empower researchers to make high-impact discoveries in cancer biology. EpigenTek offers the most comprehensive RNA methylation and epigenetic research toolkit available, with kits that are highly cited, trusted worldwide, and designed for precision, reproducibility, and ease of use.




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)