Once thought to be functionally irrelevant “junk,” non-coding DNA (ncDNA) has been shown to play essential parts in modulating many important cellular processes. These regions refer to segments of a DNA molecule that do not code for proteins. NcDNA can include regulatory elements like promoters and enhancers that control when and where genes are expressed. It also includes introns, which are spliced out during RNA processing, and repetitive sequences that have various roles, such as maintaining chromosomal organization and function.
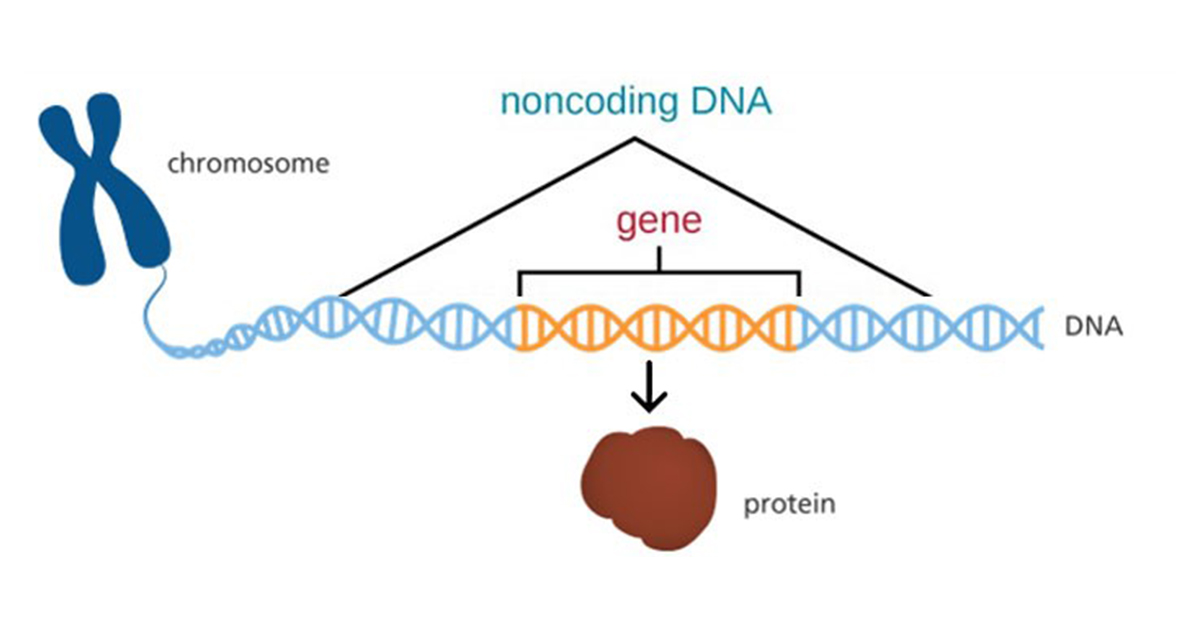
Although ncDNA does not encode proteins directly, its importance in genome activity and regulation is increasingly recognized. Methylation in ncDNA regions takes on diverse tasks in regulating gene expression, imprinting, ncRNA biogenesis, chromatin structure, and epigenetic inheritance.
Regulation of Gene Expression
Promoters are regulatory regions near the start of genes where transcription factors bind to initiate gene expression. DNA methylation at CpG sites within promoter regions can hinder the binding of transcription factors, leading to reduced gene expression or gene silencing. Enhancers, on the other hand, are DNA sequences that can be located far from the genes they regulate. Methylation at enhancers can affect their ability to interact with target genes, thereby influencing gene expression levels.
DNA methylation in non-coding regions can also influence the expression of non-coding RNAs such as long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). These can, in turn, interact with chromatin-modifying complexes to regulate gene expression in cis (near the lncRNA locus) or in trans (at distant genomic loci). LncRNAs can participate in chromatin remodeling, transcriptional activation or repression, and RNA processing.

Imprinted Genes
Imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon where the expression of a gene depends on whether it was inherited from the mother or the father. DNA methylation in non-coding regions, particularly imprinting control regions, is crucial for establishing and maintaining this monoallelic expression pattern. Imprinting disorders can arise when these methylation patterns are disrupted.
Chromatin Structure
NcDNA regions contribute to the overall organization and structure of chromatin, which regulates the accessibility of DNA to transcription factors and other regulatory proteins. DNA methylation can alter chromatin structure by recruiting proteins such as methyl-CpG binding domain proteins and histone-modifying enzymes.
Methylation of non-coding regions can lead to the formation of heterochromatin, a tightly packed form of chromatin associated with gene silencing. This structural change can persist through cell divisions, influencing long-term gene expression patterns.
Epigenetic Inheritance
DNA methylation patterns in non-coding regions are often stable and can be consistently passed to daughter cells during cell division. Maintenance methyltransferases ensure that methylation patterns are preserved, contributing to cellular memory of gene expression states. In some cases, DNA methylation patterns established in non-coding regions can be inherited across generations, influencing phenotypic traits without changes in the underlying DNA sequence.
Research Tools for Methylated DNA Analysis
DNA methylation ELISAs offer a high-throughput, cost-effective means of analyzing a variety of modified DNA forms. As pioneers in the R&D of epigenetics-based research tools, EpigenTek has leveraged its proprietary MethylFlash technology to develop rapid, accurate, and highly cited quantitation immunoassays for global DNA methylation analysis. The MethylFlash™ Global DNA Methylation (5-mC) ELISA Easy Kit and MethylFlash™ Global DNA Hydroxymethylation (5-hmC) ELISA Easy Kit have been specially designed to use fully intact input DNA as starting material, eliminating the need for additional sample processing (e.g., denaturation, fragmentation) required by similar assays. These kits combine the convenience and speed of ELISA with high sensitivity, specificity, universality, accuracy, and flexibility, making them valuable tools for researchers studying global DNA methylation in various contexts.




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)