Instructions
Western blot (WB) is a technique used to identify and localize proteins based on their binding ability to specific antibodies. First, proteins are denatured and then separated by SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis. The separated proteins are then stained by the PVDF or nitrocellulose membrane, and then blocked with milk (or another blocking reagent). The membrane is then stained with a secondary antibody specific to the primary antibody, which can be detected by a variety of methods. When compared to a ladder or size marker (in kDA), protein size and expression can be determined.
Solution and reagents
| 30% Acrylamide (makes 500 ml) | |
| Acrylamide | 145 g |
| Bis-acrylamide | 5 g |
| Fully dissolve the compounds at 37℃. Then add water for a total volume of 500 ml and store in a brown bottle at RT. | |
| pH 8.8 Tris-Hcl (makes 500 ml) | |
| Tris-base | 90.75 g |
| Fully dissolve the compounds. Adjust pH to 8.8 with concentrated HCl. Add water for a total volume of 500ml. | |
| pH 6.8 Tris-Hcl (makes 500 ml) | |
| Tris-base | 90.75 g |
| Fully dissolve the compounds. Adjust pH to 6.8 with concentrated HCl. Add water for a total volume of 500 ml. | |
| Sample 6×loading buffer (makes 15 ml) | |
| Tris-Hcl (pH 6.8) | 6% (V/V) |
| SDS | 4% (W/V) |
| Bromophenol blue | 0.2% (W/V) |
| Glycerol | 20% (V/V) |
| DTT | 9% (V/V) |
| Fully dissolve the compounds. Add water for a total volume of 15 mlNote: loading amount of protein sample should be 10-40 μg per well. Overloading protein can cause smearing. | |
| Concentrate gel (makes 4ml) | |
| 30% Acrylamide | 0.67 ml |
| Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) | 0.5 ml |
| ddH2O | 2.7 ml |
| 10%SDS | 40 μl |
| 10%APS | 40 μl |
| TEMED | 6 μl |
| Dissolved 0.1g SDS in 1ml ddH2O by heating to 56℃. 0.1 g APS is dispersed in 1 ml ddH2O and should be prepared when it will be used. 10% APS and TEMED are an accelerator which should be rapidly mixed and poured into the device. | |
| Separate gel (makes 10ml) | ||||
| MW of target protein | 70-200 | 25-70 | 20-35 | 10-20 |
| Gel percentage | 8% | 10% | 12% | 15% |
| 30% Acrylamide | 2.5ml | 3.33ml | 4ml | 5ml |
| Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) | 2.5ml | 2.5ml | 2.5ml | 2.5ml |
| ddH2O | 4.85ml | 4.02ml | 3.3ml | 2.3ml |
| 10%SDS | 100μl | 100μl | 100μl | 100μl |
| 10%APS | 100μl | 100μl | 100μl | 100μl |
| TEMED | 6μl | 6μl | 6μl | 6μl |
| 0.1g SDS is dissolved in 1 ml ddH2O by heating to 56℃. | ||||
| 0.1 g APS is dispersed in 1ml ddH2O and prepare when required. 10% APS and TEMED are catalysts, and should be rapidly mixed and poured into the device. | ||||
| Running buffer (makes 1000 ml) | |
| SDS | 1 g |
| Tris-base | 3 g |
| Glycine | 14.4 g |
| Fully dissolve the compounds. Add water to make up to 1000ml. pH 8.3 | |
For the protein weight lower than 20 kD, Trincine buffer is recommended, the recipe as follow:
| Reagent | Mass(g) | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anode buffer(1L buffer system) | Tris | 24.228 | Dissolve Tris in ddH2O, mix thoroughly and adjust pH to 8.9. |
| Cathode buffer(1L buffer system) | Tricine | 17.92 | Dissolve reagent in ddH2O, mix thoroughly. |
| Tris | 12.114 | ||
| SDS | 1 |
| Transfer buffer (wet, makes 1000ml) | |
| Tris-base | 2.43 g |
| Glycine | 11.26 g |
| Methanol | 200 ml |
| Fully dissolve the compounds and mix. Add water to make up to 1000 ml. Store in dark. | |
| Blocking buffer (makes 1000 ml) | |
| Casein | 10 g |
| Fully dissolve the compounds and mixed up. Then add 1×PBS to make up to 1000 ml. | |
| Antibody dilution buffer (makes 1000 ml) | |
| Blocking buffer | 1000 ml |
| Tween-20 | 500 μl |
| Fully dissolve the compounds and mix up. | |
Sample preparation
Preparation for lysate of cell culture
- Place cell culture dish on ice and wash cells with ice-cold sterile PBS.
- Lyse cells by adding RIPA buffer (1 mL for per 10cm dish) containing fresh protease inhibitors. Keep on ice for 15-30 min. Scrape cells and transfer to a microfuge tube.
- Sonicate the cell suspension to shear DNA and complete cell lysis (the time of sonication varies with cell type).
- Spin at 12,000 RPM for 15-20 min at 4℃.
- Transfer the supernatant into a new tube. Keep on ice at all times.
- Use BCA assay to measure the protein content in the supernatant.
- Add 6x sample loading buffer to the supernatant depending on the protein content and amount of protein needed to load on.
- Boil samples for 5 min at 95℃ (unless noted otherwise).
- Centrifuge for 5 min 12,000 RPM and store at -20℃.
Preparation for lysate of tissue
- Dissect the required tissues on ice and wash away the excess blood.
- Place the fresh tissue in a clean mortar, use liquid nitrogen to grind tissue. Collect the tissue powder into a precooling tube.
- Add RIPA buffer according to the amount of tissue (500μl for 50 mg tissue) and incubate on ice for 15-30 min with intermittent mixing.
- Sonicate the supernatant on ice (time varies depending on the tissue), then incubate on ice for 15-20 min.
- Spin at 12,000 rpm for 15-20 min at 4℃.
- Transfer the supernatant into a new tube. Keep on ice at all times.
- Use BCA assay to measure the protein content in the supernatant.
- Add 6x sample loading buffer to the supernatant depending on the protein content and the amount of protein needed to load on.
- Boil samples for 5 min at 95℃ (unless noted otherwise).
- Centrifuge for 5 min 12,000 RPM and store at -20℃.
Preparation of Gel
- Assemble the glass plates and spacers (1.5 mm thick).
- Pour an agarose plug (1-2 mm).
- Pour the running gel to about 1 cm below the wells of the comb (~20 ml). Ensure there are no bubbles.
- Seal with 1 ml water-saturated 1-butanol.
- When gel has set, pour off the butanol and rinse with deionized water.
- Pour the stacking gel (~5 ml) and insert the comb immediately.
- When the stacking gel has set, place in gel rig and immerse in buffer.
- Flush the wells out thoroughly with running buffer before running the gel.
- Follow the table below to determine which gel content you require.
| Protein size(kD) | Gel percentage |
| 15-45 | 15% |
| 20-55 | 12% |
| 25-70 | 10% |
| 70-200 | 8% |
Running the gel
- Flash-spin the samples to remove impurities.
- Load 10-30 μg of total protein into the wells. We recommend 10-100 ng of purified proteins. Loading quantities should be adjusted according to the result.
- Molecular weight markers should be included in a lane to indicate the protein of interest.
- Run with constant voltage (voltage set at 120 V or lower). To obtain a better experimental result, 80v is recommended when the whole protein migrates in concentration gel. While the proteins migrate into separation gel, voltage should be boosted up.
- Usual running time is about 80 mins, however, if the protein weight is lower then 20 kD, the runtime should be shorter, and if the protein weight is larger than100 kD, the runtime should be longer to ensure a better separation of proteins.
Transfer and Blocking
- Carefully separate the gel.
- Layer filter paper-gel- filter paper, creating a “sandwich” (see image below). Keep the “sandwich” hydrated and avoid bubbling between layers:
- Assemble the transfer device, and transfer proteins to nitrocellulose or PVDF membrane. We recommend a 0.22 μm membrane for proteins with weights lower than 20 kD.
- There are two transfer methods: wet transfer or semi-dry-transfer. Both methods work well for high molecular weight and low molecular weight proteins. However, semi-dry-transfer can yield a higher background staining.
- Rinse the blot in PBS for approximately 5 mins.
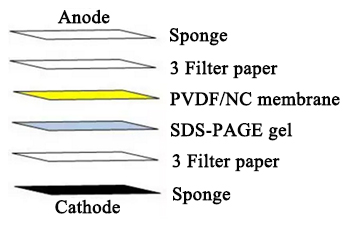
Western Blot layers courtesy of Cusabio. Click to enlarge.
Antibody incubation
- Dilute the primary antibody in blocking buffer and incubate 1-3 hours at room temperature, or overnight at 4℃. We recommend incubating at a low temperature over a long period of time, as overnight incubation typically yields improved antibody binding.
- Wash the membrane in PBST for 10 min for three times and apply the diluted conjugated secondary antibody in blocking buffer (as per manufacturer’s instructions) and incubate 1 hour at room temperature.
- Wash the blot in PBST three times for 10 min each.
Detection
- Apply the detection reagent of choice in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
- To minimalize signal reduction, mix chemiluminescent reagents in prior to use to limit light exposure and degradation.




 Cart (0)
Cart (0)













